-- Wizard 컨트롤을 사용하다가 Backspace라던지 브라우저의 뒤로가기 버튼 등으로 인해서
내가 원하는 데이터가 중복되어서 들어가거나 예상치 못한 오류가 발생하기도 하였다.
국내 사이트에서는 이러한 방법에 대한 해결 방법이 나와있는 Article이 많이 없었다.
결국 Googling을 통해서 발견한 사이트의 글이다.!!
Disable the Browser Back Button in your ASP.NET Applications
July 26, 2009 — Leonard LobelIf you’ve just come to accept the Back button as a necessary evil, I’ve got a few simple solutions for you that prevent the user from backing up past a designated “one-time only” page in your application.
For example, if you have a wizard with multiple steps, it’s fine to let the user click the browser’s Back (and then Forward) buttons all they want as they navigate from page to page. But when they click Finish on the last page, and you save information to the database, you don’t want them to be able to click Back to the last wizard page and then click Finish again. This would result in repeating the server side processing (in this example, saving to the database again, but in another scenario this could mean charging a credit card multiple times). The proper approach would be for the user to start the wizard over from the beginning, if the intent is really to submit another new request that’s entirely separate from the last one.
Disabling the browser cache for the page is not a real solution (though I’ll show it anyway), because the user gets an ugly message when they click Back. In this post, I’ll show you how to add just a tiny bit of code to achieve an ideal solution that effectively disables the Back button.
Solution 1: Ask the user nicely and hope they listen
Most developers think there’s no way to disable the browser’s Back button and just don’t even try at something they believe to be futile. And that’s why you see messages like “Please don’t click the browser’s Back button after confirming your purchase as doing so may result in a duplicate charge to your credit card” on practically every e-commerce site on the Web. Surely there’s a better way…
Solution 2: Disable caching for the page
OK, so let’s just not cache the page with the Finish button, the one that does all the work that we don’t want repeated should the user click Back and then resubmit. We can do that by overriding the OnPreInit method (same thing as, but more efficient than, handling the PreInit event) and setting the various caching-related properties on the Response object to prevent the browser from caching the page:
protected override void OnPreInit(EventArgs e)
{
base.OnPreInit(e);
Response.Buffer = true;
Response.ExpiresAbsolute = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-1d);
Response.Expires = -1500;
Response.CacheControl = "no-cache";
Response.Cache.SetCacheability(HttpCacheability.NoCache);
}
See http://forums.asp.net/t/1060173.aspx and http://www.codeproject.com/KB/aspnet/NoCaching.aspx for more information on these property settings.
One problem solved (no more risk that the user will click Finish twice), but a new problem is created (user gets “Webpage has expired” error if they click Back):
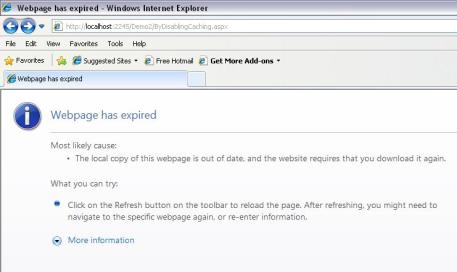
The screen shot above is from Internet Explorer; different browsers (Chrome, FireFox, etc.) handle the condition by prompting the user in different ways. But the bottom line is that this solution results in a degraded user experience because we’re not really disabling the Back button. We’re just preventing the page from being stored in the browser history, so that when the user does click the Back button, they get the expired error/prompt instead of the page they expected to go back to. Is there a way around this? You bet! Read on…
Solution 3: Disable the Back button completely
This is the simplest solution that disables the Back button completely. How simple? Just add onload=”window.history.forward();” to the <body> tag in the page(s) that you don’t want the user to be able to click Back to.
<body onload="window.history.forward();">
With this solution, the page tries to move forward in history as soon as it loads. Of course, for newly served pages this has no effect, since there’s no forward history. But when the user clicks the Back button to reload the same page from the browser history, the page immediately forces the browser to pop back to where the user came from, as though they clicked Forward right after clicking Back. But it happens before the previous page even has a chance to load because the ”forward” command is invoked on the onload event of the previous page. Including this in every page in your application will disable the Back button completely (for postbacks too), which may not be something you want. Since users do expect to be able to use the Back button, you should let them do so except when undesirable behavior results (such as charging their credit card more than once).
Solution 4: Use this “hidden field/script/postback” trick
This solution is a little more involved, but is more flexible and opens up other interesting possibilities (for example, it gives you greater control when server-side validation is involved).
The gist of it? — You can’t directly disable or otherwise control the behavior of the Back button. But you can deliver a page that always forces a redirect, which gets stored normally in the browser’s history, such that when the user clicks Back, the redirect will always be forced.
Here’s the recipe:
1) Add a hidden field
In the .aspx markup, add a hidden field server control to your page that starts off with no initial value:
<input type="hidden" id="hidIsCommitted" runat="server" />
This field will get set only when the code-behind performs the processing you don’t want repeated (e.g., database save, credit card charge) if the user clicks Back and then resubmits.
2) Just beneath the hidden field, add the following script:
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
if (document.getElementById('<%= this.hidIsCommitted.ClientID %>').value == '1')
{
location.href = 'ThankYouPage.aspx';
}
</script>
This simple code tests the value of the hidden field, and if it is set, the code redirects the user to the Thank You page (the page the user is normally redirected to after clicking Finish). Of course, the hidden field is not initially set, since we added it above with no value and no code has set its value yet.
Note the importance of using both document.getElementById and the bee-sting <%= %> server-side replacement markup for the hidden field’s ClientID value. Using getElementById ensures cross-browser compatibility, and the ClientID property resolves to the actual ID generated for the hidden field in the DOM, which includes additional unique identifiers if the element is contained inside a templated control, content placeholder, or other naming container.
3) Just beneath the script, add the following server-side span element with another script block inside of it:
<span id="spnCommitScript" runat="server" visible="false">
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
document.getElementById('<%= this.hidIsCommitted.ClientID %>').value = '1';
var theForm = document.forms['form1'];
if (!theForm) theForm = document.form1;
theForm.submit();
</script>
</span>
This code sets the hidden field value and then performs a postback, but because the script block is wrapped inside of a server-side span element named spnCommitScript whose visible property is set to false, this code is not actually sent to the client. Only when the span element is made visible by server-side code will this client script get sent to the client, and the server-side code will not make the span visible until after completing the processing that occurs when the user clicks Finish.
4) In the code-behind, just at the point in time when you have completed processing (saving to the database, charging the credit card, etc.), make the span visible. Basically, this is the same point in time that you would normally issue a Response.Redirect to the Thank You page. But instead, you just make the span visible:
protected void btnFinish_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!this.PerformAdditionalValidation())
{
this.lblValidationErrorMessage.Visible = true;
return;
}
// Update database, charge credit card, etc.
this.spnCommitScript.Visible = true;
}
The result? When the page returns to the client, the hidden field value is still not set. So the initial JavaScript test still returns false and the user does not get redirected to the Thank You page yet. But right after that, additional JavaScript code executes that has never execute before because the span has always been invisible. And that JavaScript code goes ahead and sets the hidden field, and then invokes a postback. The page returned to the client after the postback is then stored in the browser’s history cache normally. But this version of the page has the hidden field value set which causes redirect to the Thank You page. So clicking Back from the Thank You page results in reloading a page that forces itself to redirect immedately back again to the Thank You page. If the user clicks the Back button all day long, they won’t be able to back up past the Thank You page. Even if they advance several pages forward in the application, they’ll be able to click Back only up until reaching the Thank You page, but no further back than that.
All of the markup in steps 1, 2, and 3 can be placed in a Master page, so that it can be shared by all Content pages. With this approach, you would implement the redirect page as a variable rather than hard-coded as ThankYouPage.aspx and thus achieve an extremely lightweight framework for handling the Back button in this manner across your entire application. Only the code in step 4 (modified to also set the desired redirect page name) needs to be applied whereever you’d normally code an ordinary Response.Redirect in your code-behind.
Hope this information saves you some grief trying to cope with the Evil Back Button!
출처 : Lenni Lobel on .NET and SQL Server Development의 블로그!!







